
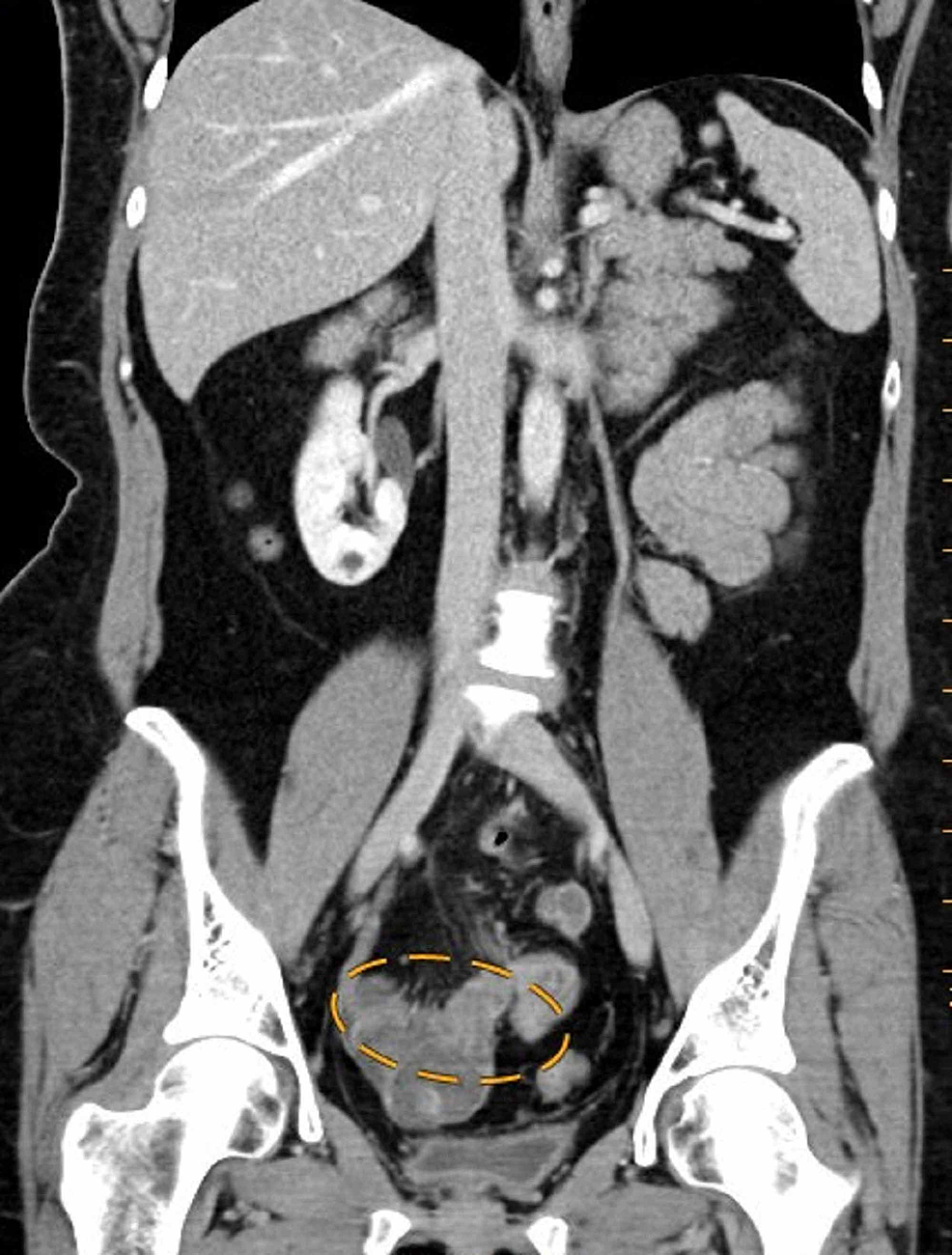
Perforation rate was 5.8% and was significantly higher in male patients (p 30 years age group (p= 0.024). Results: Out of the 4012 cases, 3530 (88%) patients showed findings consistent with acute appendicitis on HPE. Material and Methods: From January 2009 to June 2017, all histopathology reports of 4012 consecutive appendectomy specimens for a clinical suspicion of acute appendicitis were retrospectively analyzed in two university hospitals. The aim of this study was to assess whether a routine HPE of appendectomy specimens is needed and whether routine HPE has an impact on further management of patients. However, the need for routine histopathological examination (HPE) of all appendectomy specimens has recently been questioned. Objective: For a suspected diagnosis of acute appendicitis, appendectomy is one of the most common emergency abdominal operations performed. Luke’s Hospital, Kilkenny, IrelandĢDepartment of General Surgery, Benghazi Medical Center, Benghazi University, Benghazi, LibyaģDepartment of General Surgery, Al-jala Hospital, Benghazi University, Benghazi, Libya Abstract Osama Elfaedy 1, Mohamed Benkhadoura 2, Akrem Elshaikhy 3, Khaled Elgazwi 3ġDepartment of General Surgery, St. Occasionally, however, appendiceal neoplasia that is secondary from another site may dominate the clinical picture and lead to potential pathologic misdiagnosis as primary appendiceal disease.Impact of routine histopathological examination of appendectomy specimens on patient management: a study of 4012 appendectomy specimens Secondary involvement of the appendix by carcinomas of the female genital tract, particularly ovary, and diverse other sites are in aggregate common but only rarely a clinical or pathological difficulty. Secondary involvement of the appendix by leukemia has been reported. Lymphoma affects the appendix exceptionally in children, Burkitt lymphoma is most common whereas in adults, large cell lymphomas and low grade B-cell lymphomas predominate.

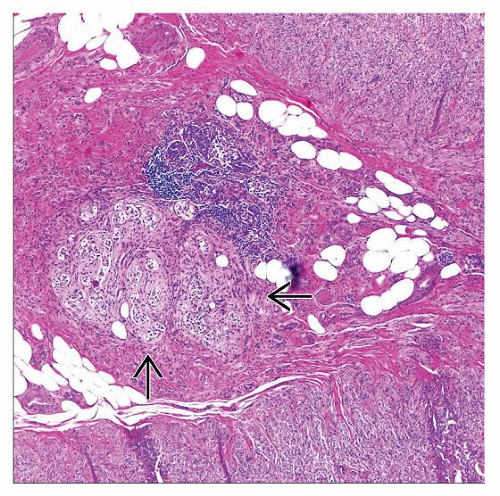
Mesenchymal tumors of the appendix are most often of smooth muscle type, usually leiomyoma but rarely leiomyosarcoma nonmyogenic neoplasms such as gastrointestinal stromal tumor, granular cell tumor, Kaposi's sarcoma, and miscellaneous other curiosities occur rarely. Neural proliferations of the appendix include lesions associated with von Recklinghausen's disease, as well as mucosal and axial neuromas that are theorized to progress to fibrous obliteration of the appendix. Vasculitis may be either isolated to the appendix or part of a systemic vasculitis, most often polyarteritis nodosa. Peritoneal endosalpingiosis often involves the appendiceal serosa and occasionally the wall but has no clinical manifestations in contrast to endometriosis. Endometriosis of the appendix, which usually occurs in the setting of generalized gastrointestinal endometriosis, often presents as acute appendicitis, but may present as intussusception, lower intestinal bleeding, and, particularly during pregnancy, perforation. Diverticular disease may be an incidental finding, but when inflamed, can be clinically confused with appendicitis. Congenital abnormalities of the appendix are rare the two most commonly reported are congenital absence and appendiceal duplication. A variety of miscellaneous conditions affect the appendix, both as incidental findings and as causes of clinical signs and symptoms that often mimic appendicitis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
